Contenido
- 1 Let’s review the neglected heroes of your construction equipment: hydraulic gear pumps.
- 2 CE Certification: Hydraulic Gear Pump Validation of Compliance
- 3 Surviving Southeast Asia: Monsoon Conditions of Hydraulic Gear Pumps
- 4 The Dirty Truth About Lifecycle Costs: Why a $500 Pump Can Cost $5,000 in Two Years If You Neglect These Three Parts
- 5 Hydraulic Gear Pump FAQ: Stop Your Most Frustrating Issues
- 5.1 1. “What Are The Different Methods of Stopping Hydraulic Gear Pump Leaks?”
- 5.2 2. “How Do Desiccant Breath Filters with 5 Micron Pre Filters Work?”
- 5.3 3. “What Is The Purpose of A Coupling?”
- 5.4 4. “Is A Material Certificate Compulsory For Every Product?”
- 5.5 5. “Can I Safely Extend Maintenance Intervals?”
- 5.6 6. “What are the Three Warning Signs I Should Look Out For That Indicate An Entire Pump Replacement?”
- 5.7 7. “Who Wins Piston Pump and Gear Pump Showdown?”
- 5.8 1. 24/7 health monitoring with a preset alarm.
- 5.9 2. Automatic slack compensating wear structures.
- 5.10 3. Oil quality monitoring AI.
- 6 The Ultimate Checklist for Selecting a Hydraulic Gear Pump
Let’s review the neglected heroes of your construction equipment: hydraulic gear pumps.
Maintenance engineers dealing with high-pressure hydraulic systems know how critical selecting the right pump is. Today, I will cover all that is required for selecting a PLC-compatible, rugged, 16cc/rev external gear aluminium pump.
Why Prefer External Gear Over Other Pumps?
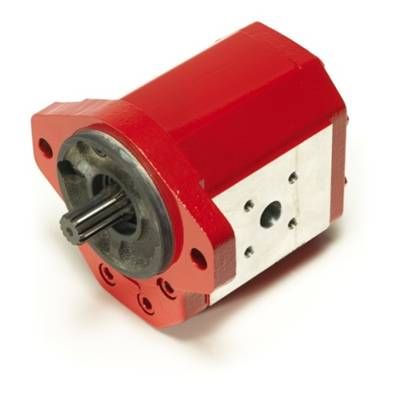
No one can deny that external-gear hydraulic gear pumps are essential components. They consist of two meshing interlocking gears, one driven and one idle, which transport oil from the inlet to the outlet. Is this complex? Of course not; is this effective? Absolutely. As with most internal gear designs, they are able to handle high pressures (up to 250 bar) and viscous fluids far better than most internal gear designs. And, because of the aluminium housing, these pumps are much lighter and still durable, which is crucial to mobile machinery.
But here is the kicker: internal-gear pumps such as Gerotor types are very quiet; however, they are highly susceptible to contamination. A single crushed particle of silica will potentially cost you a new rotor set. However, external gears are able to handle modest debris with ease and continue functioning without problems. There is no denying the trade-off of external designs being louder and slightly less efficient, but on construction sites, dependability far outweighs quiet operation.
Additionally, this is how CE certification can disturb your pump range selection combined with a horror story from a Malaysian cement plant.

CE Certification: Hydraulic Gear Pump Validation of Compliance
When operating in Europe or obtaining parts from a supplier in a different part of the world, the CE marking is not optional as it is a requirement. For hydraulic gear pumps, the EU Machinery Directive (2023/1230) and Pressure Equipment Directive (PED 2014/68/EU) have defined the parameters. For your 16cc/rev pump, these are the critical aspects:
Explosion-Proof Ratings
Facing leaks head on, high-pressure hydraulic systems are notorious for these “accidents.” CE-certified pumps mandate IP66 seals and burst-pressure testing at 1.5x max operating pressure. No more “oops” moments when a hose blows at 200 bar.
Material Traceability
CE-certified hydraulic gear pumps must have traceable documents. The aluminium housing certifies mill certificates proving it’s EN 1706 compliant mon alloys that are known to thermally cycle crack. I have seen $20K excavator hydraulic pumps sink due to those alloys in weeks.
PLC Integration
Pumps that interface with PLCs need to comply with Directive 2014/35/EU, thus requiring EM shielding. Skip this, and your control signals will drown in electromagnetic noise from nearby diesel generators.
A Real-World Cautionary Tale
A Thai contractor once installed non-CE pumps in tower crane hydraulics. Six months down the line, saltwater humidity had rusted the shafts, which led to catastrophic failures during lift loads. The solution? Retrofitting CE-rated pumps for the entire system brought the cost to €230K. Compliance isn’t bureaucracy; it’s insurance.
Surviving Southeast Asia: Monsoon Conditions of Hydraulic Gear Pumps
Facing the facts—excessive humidity, sea salt, and monsoons convert standard hydraulic systems into heaps of rust. I recall pumping failures within three months at Indonesian coal mines due to the lack of adherence to environmental specs. Here is how to extreme-proof these 16cc/rev pumps for tropical hellscapes:
Material Warfare
Cast iron vs Aluminium: While Aluminium might resist corrosion Marines grade anodising (Mil-A-8625 Type III) is a requirement in coastal areas.
Shaft seals: Nitrile seal rot within humid conditions, switching to FKM (Viton?) seals works wonders. Though they are 30% more expensive, they last 5 times longer in lots of humidity.
The Contamination Crisis
Monsoon mud drowns pumps. Any pumps with filters under 10 micron rated absolutely need bypass filtration loops with a beta ratio over 200. For bonus points, palm oil plantations in Malaysia started using magnetic drain plugs to remove ferrous sludge before the gears get a hold of it.
Surviving Thermal Shock
Housings are prone to warping under Vietnam’s 40-degree-25-degree downpour extremes.
They can be PLC-controlled to gradually increase pressure step by step.
Mounting flanges placed with silicon-based grease allow quick dissipation of overheating.
Estudio de caso
A certain port in Singapore experienced recurring breakdowns of a container stacker’s pumps every eight weeks. The implementation of ceramic coated gears and desiccant breathers increased the lifespan to 18 months. ROI? 142 percent.
The Dirty Truth About Lifecycle Costs: Why a $500 Pump Can Cost $5,000 in Two Years If You Neglect These Three Parts
The lesson on lifecycle costs is titled: “The $5000 Lesson in Cheap Pumps.”
Discount hydraulic gear pumps are gambles in which no rational individual would stow away using a subpar budget parachute. I’ve disassembled enough failed units to understand that 90% of “unexpected” failures stem from three ignored components. Let’s explore the costs associated with a 16cc/rev pump over five years.
1. Bearing Betrayal
Cheap Bearings: $20 per unit offshore bearings with no ABEC rating are a mistake. These offshore-made bearings shrunk in performance when subjected to high side-loads at a rate of 4x.
Cost Impact: Out of a total 30-pump fleet, these pumps incurred $36,000 in needless bearing replacement costs over the 5-year span due to frequent needed repairs.
Labour costs of $500 per pump roughly translate to $250,000 over 5 years, further escalating the costs in having to pay these maintenance expenses through cash for capex.
2. Seal Sting
Standard Lip Seals: Under consistent high pressure pulsation, they fail within a year or less.
Upgraded Option: PTFE dynamic seals, while costing 2.5x more, offer reliability and durability lasting 60,000 operating hours validated through ISO 18752 testing.
3. Gear Tooth Fatigue
This refers to the uncoated gears which suffer from pitting due to severely contaminated oil. They are also pitted due to 15,000 cycles.
Applying these upgrades could yield savings up to and around $1000 per pump. Through amortisation of these additional expenses and projecting them along the pumped growth trajectory, it gets easier to justify expense-derived pump savings.
Answer
The addition of a DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) coating increases the cost of a pump by $300, however, it triples the lifespan of the pump in harsh abrasive conditions.
Total Cost Analysis
| Component | Budget Pump | Smart Upgrade |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | $500 | $1,100 |
| 5-Year Repairs | $4,300 | $700 |
| Total | $4,800 | $1,800 |
A mining company from the Philippines demonstrated this with what they referred to as “cheap” pumps; these pumps were 63% more expensive over 3 years compared to premium units.
Above all, these are your top seven questions on hydraulic gear pumps, including how to stop that dreadful whining noise.
Hydraulic Gear Pump FAQ: Stop Your Most Frustrating Issues
I know how difficult it can be to troubleshoot bombas hidráulicas with a gear system on construction sites. From Jakarta to Johannesburg, I have worked on construction sites all over. Below, I outline the most pressing concerns that engineers tend to lose sleep over, including:
1. “What Are The Different Methods of Stopping Hydraulic Gear Pump Leaks?”
Be sure to inspect the shaft seal first, as 80% of hydraulic leaks stem from that source. Use a laser thermometer, and if the seal area shows a >10°C differential in temperature from the housing, it is failing.
Torque Matters: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for Paj Nm specs, as over tightening or under tightening can hinder performance.
2. “How Do Desiccant Breath Filters with 5 Micron Pre Filters Work?”
These pumps will not work with standard 5-micron filters or breathers.
Positive Pressure Solution: Some German quarries now use 0.2 bar air purge systems to keep a positive pressure in the reservoir preventing dust ingress.
3. “What Is The Purpose of A Coupling?”
In my experience, there are more misaligned drive couplings instead of cavitation causing the banshee noises. Aligning drive couplings mitigates 40% of the noise.
Quick Fix: Dampeners need to be added immediately, especially the ones made from hydraulic hose loops.
4. “Is A Material Certificate Compulsory For Every Product?”
You could justify spending a lesser amount on a $200 pump, but basic check spectroscopy is required for verification.
Hidden Costs: In my experience, many cheap pumps require custom mounting adapters which add $150+, unabashedly nullifying the “bargain” price.
5. “Can I Safely Extend Maintenance Intervals?”
Crucial Oil Analysis: One contractor in Dubai leaps from a 500 hour to an 800 hour interval due to the onsite viscosity testers they utilize.
Be Certain Not To Skip: Preventative seal inspections every 250 hours ensure 90% failure mitigation and only require 15 minutes.
6. “What are the Three Warning Signs I Should Look Out For That Indicate An Entire Pump Replacement?”
Noticeable Efficiency Reduction:
- Decrease in efficiency below 85% (monitor the flow rate and amp draw)
- Case drains >10% of overall flow.
- Oil metal concentration over 50 ppm (atomic emission testing).
7. “Who Wins Piston Pump and Gear Pump Showdown?”
Gear pumps rule lean hydraulic driving of conveyor belts and other simple uses needing high-speed performance.
In applications requiring a pressure greater than 300 bar or variable displacement, go with a piston pump.
*2025’s self-diagnosing smart pumps predict failures up to a month in advance.*
It was at last month’s Hannover Messe that I had the pleasure of experiencing Bosch Rexroth’s new gear IoT pump. This innovation is set to change the way we care for hydraulic systems. Here’s everything you need to know:
1. 24/7 health monitoring with a preset alarm.
Sensors fitted to the pumps allow health monitoring:
- Vibration sensors notify bearing failure VRB: bearing sensing 30 days in advance by monitoring harmonics.
- Pressure transducers: detect leaks internally for as sensitive as 0.5 cc/rev which is 10x more than manual tests.
2. Automatic slack compensating wear structures.
The game changing innovation in 2025 is going to be clear shape memory alloys.
No longer this nonsense:
- ? shim replace adjustment
- ? premature shim replacements from guesswork backlash
3. Oil quality monitoring AI.
Pumps can now alert users when water exceeds the 0.15% threshold because systems integrated microuid sensors that
- Monitor and alert every quarter hour for viscosity changes
- Predict additive depletion (like ZDDP) with +/- 5% precision.
Results gathered in the field:
- 62% drop in unexpected downtimes
- Oil change periods increased 2.3X
- Seal failure incidences decreased by 81% due to predictive pressure spike alert for spiking limits (quote).
The Ultimate Checklist for Selecting a Hydraulic Gear Pump
Having worked in the field for 20 years, I’ve created a 7-step procedure to guarantee you never purchase the wrong pump again. Print this and put it in your toolbox:
1. Pressure Profile Mapping
Looking at maximum pressure isn’t enough – make sure you capture pressure spikes with a 100ms-sampling data logger.
Add a 25 percent margin on top of your highest recorded spike for safety.
2. Contamination Defence Plan
For dusty locations: Demand for an ISO 4406 18/16/13 cleanliness rating as minimum.
IN marine environments: request for stainless steel shaft sleeves.
3. Thermal Reality Check
Measure actual reservoir temperatures for 72 hours.
If oil exceeds 65 degrees Celsius for more than 30 minutes per day, you need:
- ? Bigger housing
- ? Cooling fins
- ? Upgrade to synthetic oil
4. PLC Integration Proof
EMC immunity verification to:
- ? 30V/m RF fields
- ? 2kV voltage surges
- ? 100A ground loops
5. Maintenance Access Audit
Check:
- ? Change the seal without removing the pump
- ? Standard tool access to drain ports
- ? Nameplate data visibility post-installation
6. Spare Parts Vetting
Find 3 or more locations globally stocking:
- ? Gear sets
- ? Shaft seals
- ? Mounting hardware
7. Failure Mode Review
Demand the FMEA reports showing:
- ? MTBF over 25,000 hours
- ? The worst possible failure is not catastrophic.
Pro Tip: An Australian miner reduced operating costs by $1.2M per year by implementing vibration logging which allowed him to identify pending bearing failures during routine weekly inspections.






