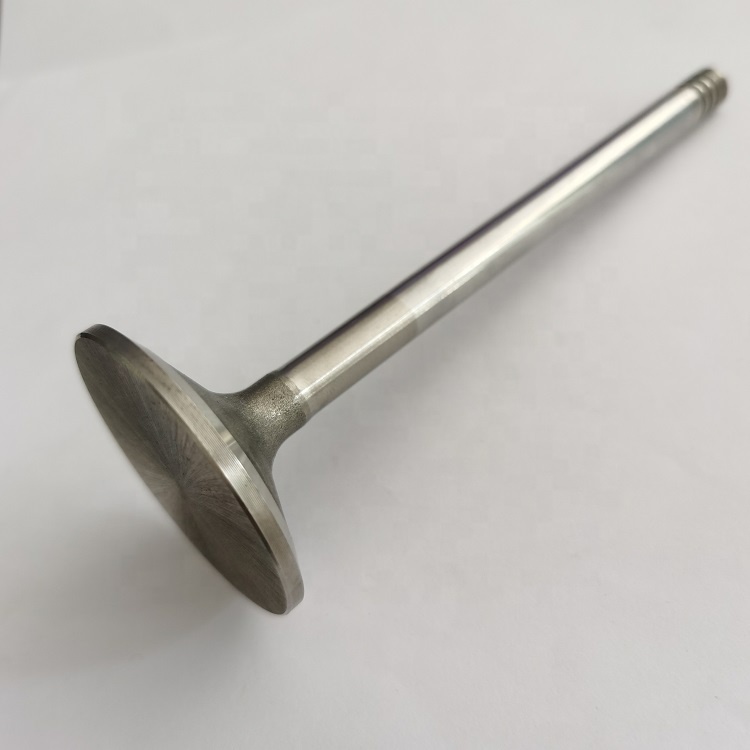
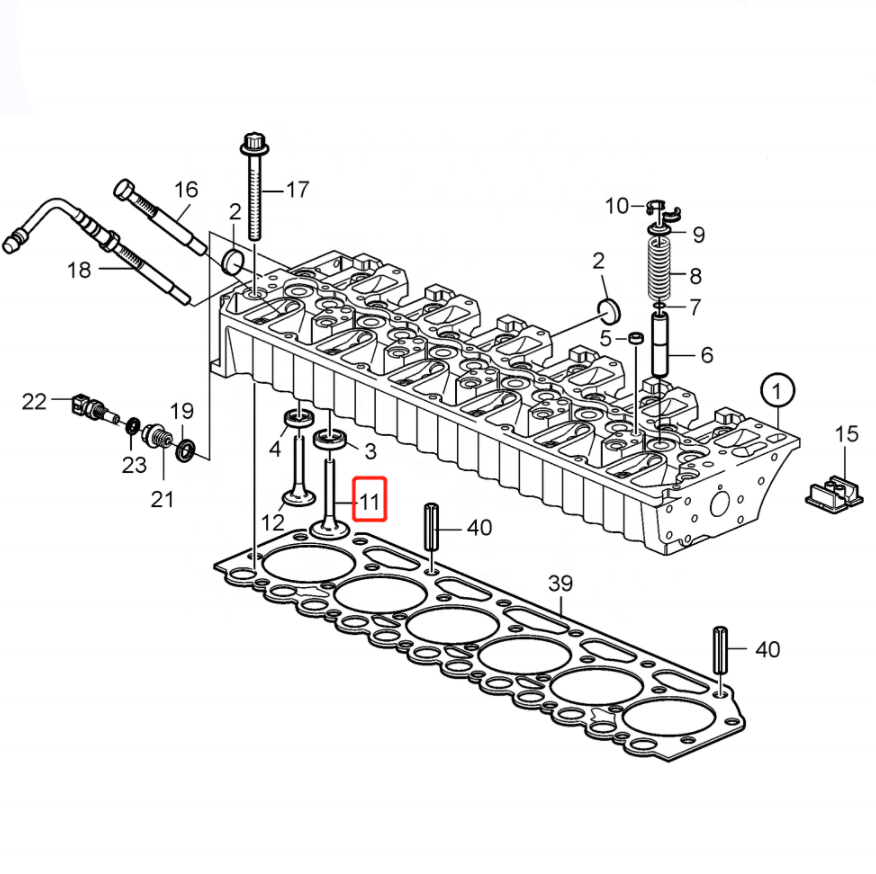
KALMAR Engine Parts 720 Intake Valve 20714469, 923976.3033, 20405503, 0428 3380, 0450 9353, 1007011-52D
The 720 Intake Valve is a critical component for controlling the flow of air and fuel into the engine
KALMAR Engine Parts 720 Intake Valve 20714469, 923976.3033, 20405503, 0428 3380, 0450 9353, 1007011-52D - Advanced Analysis
The Intake Valve is a vital component in internal combustion engines, playing a crucial role in regulating the flow of air and fuel into the engine’s cylinders. It is an essential part of the engine’s intake system, opening and closing at precise times to allow the correct amount of fuel and air mixture into the combustion chamber. The proper function of the Intake Valve is critical to engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. These valves are commonly used in automotive engines, industrial machinery, and other engine-powered devices.
The Intake Valve works in conjunction with the camshaft to regulate the timing of its opening and closing. When the valve opens, it allows a mixture of air and fuel to enter the cylinder, which is then compressed and ignited to power the engine. Once the combustion cycle is complete, the Valve closes to seal the cylinder and prevent the mixture from escaping. This precise coordination ensures that the engine runs efficiently, with optimal fuel usage and power generation. If the Intake Valve malfunctions, it can result in a range of issues, including poor fuel efficiency, reduced power, and increased emissions.
In automotive applications, the Intake Valve is typically constructed from high-strength materials such as stainless steel, alloys, or heat-resistant composites, designed to withstand high temperatures, pressures, and wear. These valves are subject to extreme conditions during engine operation, with temperatures often reaching several hundred degrees Celsius. The must also resist corrosion from exhaust gases, which makes the selection of materials and coatings critical to its long-term performance. Regular maintenance and replacement of the Intake Valve?help prevent potential engine damage caused by wear or improper sealing.
In addition to its role in fuel and air delivery, the Intake Valve also helps manage the engine’s emissions. Modern engines are designed with emission-reducing technologies that require precise control over the intake process to minimize the production of harmful gases like carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). The Intake Valve’s timing and operation influence how efficiently the combustion process occurs, and maintaining its performance ensures that emissions remain within legal limits.
The Intake Valve is also integral to the engine’s power and efficiency. Properly functioning intake valves ensure that the air-fuel mixture is delivered at the right moment and in the right quantity, optimizing the combustion process. This leads to improved engine performance, more power output, and better fuel economy. An improperly functioning valve can cause the engine to run too rich or too lean, resulting in inefficient combustion, increased fuel consumption, and reduced engine performance.
The durability and longevity of the Intake Valve are enhanced by regular maintenance, which includes cleaning, inspecting for wear, and replacing faulty valves. Over time, debris, carbon buildup, and wear from frequent cycling can cause the valve to lose its seal or fail to open and close properly, leading to poor engine performance. Symptoms of a faulty Valve include rough idling, engine misfires, decreased fuel efficiency, and increased emissions. Timely repairs and replacement of faulty intake valves are essential to maintaining the engine’s performance and avoiding costly repairs.
In conclusion, the Intake Valve is a critical component for controlling the flow of air and fuel into the engine, directly affecting engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Proper maintenance and timely replacement of the Intake Valve ensure optimal engine performance, prevent damage to engine components, and reduce the risk of operational failures. Its role in regulating the intake process is indispensable in modern internal combustion engines, whether in automotive vehicles, industrial machinery, or other engine-powered equipment.
For more information regarding the regulations and standards related to Intake Valves and other engine components, you can visit the official website of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) at https://www.epa.gov/.
Bulk Source KALMAR Engine Parts 720 Intake Valve 20714469, 923976.3033, 20405503, 0428 3380, 0450 9353, 1007011-52D
Direct Factory Pricing | OEM/ODM Customization | GRS Certified Materials